Welcome on this forum & topic
This forum is full of people with the same interest as you. ESK8 is the main part. But on some topics you can pick up some info about 3d printing, milling etc…
If you are new here I can suggest to read this topic. I know the sun is shining and it would be awesome to drive through your neighborhood. But take your time with building your first board! You better wait 2 weeks longer to have a better board.
Almost everyone is willing to help you with your questions. But I get a little annoyed by the large amount of topics that are opened by beginners.
The start of building your board starts with reading. Not purchasing parts or questions… If you have any questions after this WIKI, Then I recommend that you first use the search bar before opening a new topic with your question.
Why DIY?
With DIY boards, the user has the option to build his board according to his wishes. Along the mechanical side you can choose which deck, wheels, trucks, bearings, motor mount and gears are used. On the electronic side, the battery, BMS, motor, ESC, remote control can be selected as desired.
What do we need to build a ESK8?
The standard skateboard/longboard/mountainboard parts:
1.1 Deck
1.2 Trucks
1.3 Wheels
ESK8 relateded parts:
The three most important electronic components are the motor, the ESC and the battery.
The motor transmits the mechanical power to the wheels.
The ESC (electric speed controller) is the brain of the board, it controls the motor using the electric current from the batteries.
The batteries provide the electrical power needed to run the engine and provide sufficient torque.
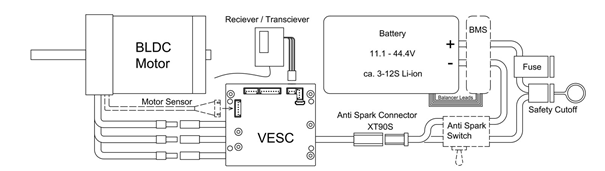
2.1 Motor
2.2 Speed controller(ESC/VESC)
2.3 Battery
2.4 Charging (BMS/Balance charger)
2.5 Remote & Reciever
2.6 Switch
2.7 Enclosure
2.8 Wires
2.9 Connectors
Safety
3.1 Fuses
3.2 Tips and Tricks
Calculators
FAQ
Example parts lists
Reputable vendors
Explanation:
1.1 Deck:
The choice of your deck depends very much on your own preference. A longer deck gives you more stability, a smoother ride and more space for your components.
You can chose if you want to have a flexible or stiff deck. If you chose for a flexble deck, keep in mind that you need to split your enclosure or build it flexble. Same for your battery and electronics. (more on this later)
1.2 Trucks:
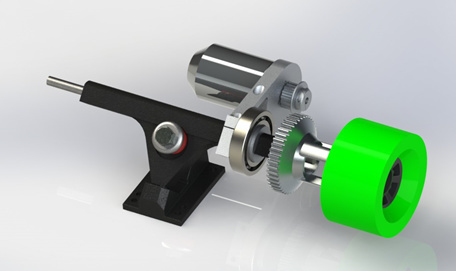
Trucks are an important part of your board. Longboard trucks are available in two versions: Reverse Kingpin trucks and Standard trucks. Most longboards are equipped with Reverse Kingpin trucks. Longboard trucks are also available in all sizes. It is recommended to use trucks that are approximately the same width as the deck. When using wider trucks, the board will drive more steadily, but cornering becomes more difficult.
The choice of trucks for electric longboards cannot be entirely as desired as with normal longboards. This is because of the motor mount. This mount is mounted on the trucks and must have a large contact surface. There are several companies that release motor mounts for specific trucks. A common truck is the Caliber brand. Due to the rectangular shape the mount fits perfectly on the truck.
1.3 Wheels:

Longboard wheels are larger than traditional skateboard wheels, making you drive faster and smoother. In addition, longboard wheels offer good vibration absorption. Smaller longboard wheels are more alert. Larger wheels are designed for a higher speed and make it easier to drive on irregular roads. All wheels also have a certain hardness. Softer wheels give you a better grip and absorption of shocks, while harder wheels are very suitable for high speed and slides. The hardness of the wheels is displayed in a durometer range between 70A(soft) and 100A (hard). For esk8 wheels we use wheels with a core inside. This makes the wheel pulley easy to assemble. Pulleys for Flywheel or Kegel wheels are easily available everywhere.
2.1 Motor:

Electric longboards use a three-phase outrunner motor. With this type of motor, the windings are the stator and the permanent magnets in the rotor rotate around it. With the inrunner motors, the permanent magnets are on the inside of the motor and rotate, while the coils are on the outside. The inrunner engines are often used with RC cars, because they run much faster. The outrunner motors run slower but generate more torque and run cooler.
To show the dimensions of these types of engines, a trend has emerged with a series of four digits (example: 6364).
The first two digits are the outside diameter of the motor and the last two the length of the motor. The larger the engine is, the more torque it will be able to provide. This is because of the length of the magnets and the space that there is for the coils.
Outrunner motors are used for electric longboards. These are connected to the ESC or VESC. An important element in choosing the right motor is the KV value (read later in this topic). The motor selected depends on the battery voltage.The motors all have a wattage between 500W and 4000W per motor. The slightly more expensive engines have, apart from the three phase cables, a fourth cable, the sensor cable. This sensor can detect the position of the rotor. This makes a smoother start possible.
There are two major differences among the motor. The unsensored en sensored motor.

An unsensored motor has 3 cables those are the phase cables. With this type of motor a push to start is necessary.

The sensored motor has 4 cables, the 3 phase cables and an additional sensor cable (split into several small cables). A sensor is connected to this cable. Thanks to this sensor, the esc can determine where the rotor is located. A smooth start without pushing is perfectly possible. This type of engine is usually slightly more expensive than the other engine.
Apart from these differences, we can still make a distinction.
For a esk8 we can use either outrunner motors or hub motors
Hub engines have appeared on the market in recent years, the motor is built into the wheel.
Advantage:
- less noticeable
- quieter than outrunners motors
- Usually cheaper
Disadvantage:
- modest choice of hub motors
- Suitable trucks required
- Urethane must make place for the motor, making a bad road surface easier to feel.
- Usually less power then outrunners.
- Maintenance is more difficult to perform
Outrunner motors are the longest on the market and are most commonly used on boards
Advantage:
- more power
- easier maintenance
Disadvantage:
- Expensiver, the correct motor mount, gears and belts are necessary
- By keeping the urethane from the wheels, the bad road is less noticeable
MOTORSPECIFICATIONS
KV: The KV value stands for the number of revolutions per minute that an electric motor makes per volt that is applied to the poles.
W: Watt is the unit for power. 1 Horse power = 736W
2.2 ESC:
The ESC is the component to which everything is connected. The ESC is powered by the battery. This voltage depends on the operating voltage of the motor.
Here on the forum we aim to use a VESC. A VESC is an open source ESC designed in 2015 by Benjamin Vedder. The VESC is specially designed for the electronic longboards. There are many advantages of a VESC over an ordinary ESC. This way the VESC can be programmed completely to size. The strength of the braking is adjustable. Many safety functions are possible such as current and temperature control. Nowadays it is easy to purchase vesc’s at an affordable price. And I see no advantage in buying normal cheap escs. Because of this I also leave this behind in this wiki.

2.3 Battery:
The battery a important part in the puzzle…
The battery in a longboard can be made of 3 types: a Li-ion battery, a Lipo battery or a Lifepo4 battery.
Li-ion:
Due to the high energy density, the Li-ion cell is mainly used in consumer electronics, such as laptops, electric bicycles and cars. The li-ion cell can be recognized by its typical cylinder shape. Where the top of the battery is the plus and the bottom the min.

The nominal voltage of the battery is usually fixed at 3.6 volts. However, this cell can vary between 2.4 and 4.2 volts. If the cell goes below 2.4 volts, it is broken. The cell has been discharged too deeply and is irreparably damaged. As a result, a safety voltage between 2.8 and 3 volts is maintained at these cells. If a cell is discharged to this voltage, nothing is wrong. When the cell is discharged to this voltage, it can be recharged. For this it is recommended to use chargers specifically for these cells. These charge the cells to a maximum voltage of 4.2 volts.
A li-ion cell has many extra advantages over other batteries. This battery has a very high energy density, low self-discharge, no memory effect and a long service life. Naturally, all advantages also have disadvantages. For example, this battery is relatively expensive to purchase, it is dangerous in the event of improper use and unprotected cells must be checked continuously.
Lipo:
The Lipo cell is a variant of the li-ion cell and is mainly used in model building. This cell has a large power available in relation to its weight. This cell also has a low internal resistance, so that it can deliver a high current. The Lipo cell is not affected by the memory effect.

Lipo batteries must be charged correctly. If this does not happen, they will break. A Lipo cell has a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts. This cell may be charged to a maximum of 4.2 volts and discharged to three volts. If this does happen, there is a good chance that the battery cannot be charged afterwards.
Capacity:
The capacity of a battery is basically a measure of how much power the battery can hold. Think of it as the size of your fuel tank. The unit of measure here is milliamp hours (mAh)(3000mah = 3Ah). This is saying how much drain can be put on the battery to discharge it in one hour. Since we usually discuss the drain of a motor system in amps (A).
ATTENTION: Watt Hours (Wh) is a better measurement of the size of a battery.
Watt Hours:
A watt-hour (Wh) is a unit of energy; it’s a way to measure the amount of work it can deliver.
The calculation is very easy: Wh = Ah * nominal voltage battery.
Watt-hour is also used in the calculation for the range off your board.
The “C” Number (Mostly used on lipo batteries)
Capacity had a direct impact on certain aspects of the vehicle, whether it’s speed or run time. This makes them easy to understand. The Discharge Rating (I’ll be referring to it as the C Rating from now on) is a bit harder to understand, and this has lead to it being the most over-hyped and misunderstood aspects of LiPo batteries.
The C Rating is simply a measure of how fast the battery can be discharged safely and without harming the battery . One of the things that makes it complicated is that it’s not a stand-alone number; it requires you to also know the capacity of the battery to ultimately figure out the safe amp draw (the “C” in C Rating actually stands for ‘‘C’’ apacity). Once you know the capacity, it’s pretty much a plug-and-play math problem. Using the above battery, here’s the way you find out the maximum safe continuous amp draw:
50C = 50 x Capacity (in Amps)
The resulting number is the maximum sustained load you can safely put on the battery. Going higher than that will result in, at best, the degradation of the battery at a faster than normal pace. At worst, it could burst into flames. So our example battery can handle a maximum continuous load of 250A.
Most batteries today have two C Ratings: a Continuous Rating (which we’ve been discussing), and a Burst Rating. The Burst rating works the same way, except it is only applicable in 10-second bursts, not continuously. For example, the Burst Rating would come into play when accelerating a vehicle, but not when at a steady speed on a straight-away. The Burst Rating is almost always higher than the Continuous Rating. Batteries are usually compared using the Continuous Rating, not the Burst Rating.
Serie connections ≈ “S” Number:
If you have read the previous paragraph correctly, you understand that a battery cell is between 3 and 4.2v. Because a voltage between 3.2 and 4.2 volts is not sufficient to drive a longboard, those cells will be placed in serie to create a higher voltage. Higher voltage means less amps need to be drawn for the same amount off power. (ohm’s law)
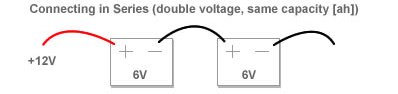
You can put a some cells in serie by connecting the positive side off the first cell to the negative side of the second cell.
The “S” number gives the amount off cells you put in serie.
Parallel connections ≈ “P” Number:
For a parallel connection you need to connect the from the first cell to the negative from the other cell. Same for the positive side. The result is two cells become essentially one. They will automatically balance each other out to the same voltage. Parallel config doubles the Ah, meaning you’ll get more capacity.
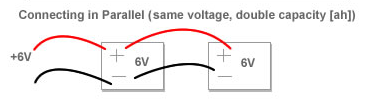
The “P” number gives the amount off cells you put in parallel.
2.4 Charging:
There are two ways to charge the batteries. You can use a BMS and “laptop” style charger or a Balance charger.
BMS:

A BMS (battery management system, Battery Management System) is an electronic system that manages a rechargeable battery (cell or battery pack) to keep the battery within its safe working area, monitor its condition, calculate secondary data, report that data and possibly to intervene, to discover errors and / or to balance them.
In topic will be people talking about high discharge BMS or charge only BMS.
A high discharge BMS means that the power to the ESC go first through the BMS.
Advantage:
- BMS will cut power when a group goes below the setted voltage cutt off
- Over current protection
- Possibilty to have a e-switch, so no need for a antispark switch
Disadvantage:
- Bigger
- Cost more
A charge only BMS is a normal BMS where the output is bypassed. So the power goes directly from the battery to the ESC
Advantage:
- Cheaper
- Take less place
Disadvantage:
- No over current protection (You can shortcuit your battery pack, External fuse is highly recommended!)
- No voltage cutt off
“Laptop” style charger

When you use a bms it is really easy to charge your battery. It is plug and play. For charging your pack you must buy the correct charger. You calculate the voltage for the charger with
max voltage from each cell * number off serie cells = voltage charger
You can buy chargers in different amperes. For the correct charging amps check out what is the weakest link. Check your datasheet from your battery pack but also that from your bms.
Balance charger:
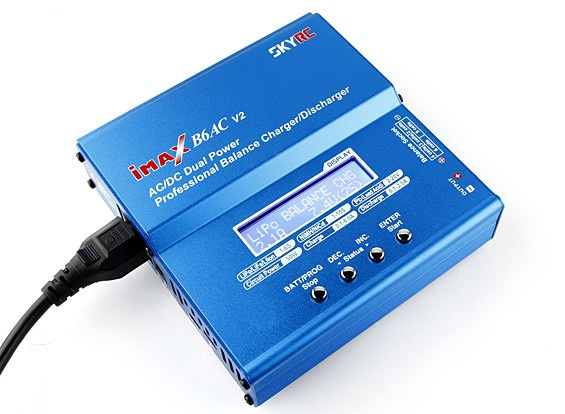

If you are not sufficiently familiar with a bms and charge adapter, you can also use a balance charger. A balance charger is cheaper and eaisier to use than a BMS
2.5 Remote:
To control your esk8 you need a remote. Please don’t cheap out on this part. It is the only communication between you and your board.
I think the most reliable remote on the market is this one:

You can also check out the Maytech remotes, Hoyt puck remote, Enertion Nano x and Flipsky remote.





But please stay away from the winning remote.

2.6 Switch:
To power off your board you need a switch. There are some vesc’s who has already a inbuilt switch.
If this is not the case, you have the choice to use an anti-spark loop key or a digital anti-spark with mosfets.


2.7 Enclosure:
To protect your batteries and other expensive parts you are going to need a solid enclosure. Key features of this should be sturdy construction and a suitable way to hold the electronics securely.
You can self build a enclosure of buy one from a shop.
2.8 Wires
For wires we use most off the time silecone wires. You can buy them everywhere you want but keep in mind this:
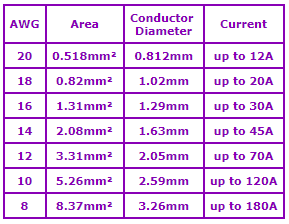

2.9 Connectors
You can use different types off connectors but mostly used are those in this list.
Power leads:
 XT60 capable off 60A
XT60 capable off 60A
 XT90 capable off 90A
XT90 capable off 90A
Motor wires:
 4mm bullets (usually standard on the vesc)
4mm bullets (usually standard on the vesc)
 5.5mm bullets
5.5mm bullets
Charge ports:
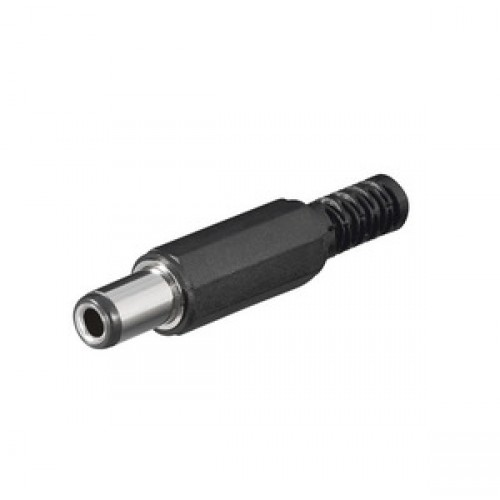 DC Power Plug Jack 2.1mm x 5.5mm capable off 5A
DC Power Plug Jack 2.1mm x 5.5mm capable off 5A
 DC Power Jack socket 2.1mm x 5.5mm capable off 5A
DC Power Jack socket 2.1mm x 5.5mm capable off 5A
 XLR Panel mount connector capable off 10A
XLR Panel mount connector capable off 10A
Safety:
3.1 Fuses
3.2 Tips and Tricks
Calculators
FAQ:
What motor should I use?
What battery pack?
What should you spend most money on?
Can I build a Li ion pack?
Example parts lists:
Reputable vendors:
General parts(A-Z)
- 3d servisas @3DServisas
- Alien power system
- Bioboards
- Electricboardsolutions
- Eskating.eu
- E-toxx
- Hobbyking
- Overion
- pwrboards.com
- street-wing.com
- Trampaboards
- Unikboards
- Psychotiller @Psychotiller
- Longhairedboy
- Torqueboards
- Build Kit Boards
- ChibatterySystems
- IdeaTB
- Unikboards
- Unconformist
- LazyRolling
- ElectricPacks @pjotr47
Batteries
Pre-built stores



 ?
?